Table of Contents
ToggleWebsite Speed Optimization: 20 Fixes That Work
Website speed is crucial in today’s digital world. Users expect website speed optimization to load within seconds, and search engines like Google reward fast-loading sites with better rankings. Slow websites can lead to high bounce rates, lost revenue, and poor user experience. Optimizing website speed is not just about technical tweaks—it’s about improving overall performance, user satisfaction, and search engine visibility. In this article, we will explore 20 actionable fixes that can help your website load faster and perform better.
1. Optimize Images
Images are often the largest files on a website and can significantly slow down page load times. Use tools like TinyPNG or ImageOptim to compress images without losing quality. Additionally, serve images in next-gen formats like WebP, which are smaller and faster to load. Ensure images are scaled correctly for different devices to avoid unnecessary bandwidth usage.
2. Enable Browser Caching
Browser caching allows returning visitors to load your website faster by storing static resources like CSS, JavaScript, and images locally. You can set cache expiration times in your website’s .htaccess file or through plugins if you’re using WordPress. This reduces repeated requests to the server and improves load times for repeat visitors.
3. Minify CSS, JavaScript, and HTML
Minification removes unnecessary characters like spaces, comments, and line breaks from code files. This reduces file sizes and speeds up loading. Tools like UglifyJS, CSSNano, or online minifiers can help. Many WordPress plugins, such as Autoptimize, also perform minification automatically.
4. Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN)
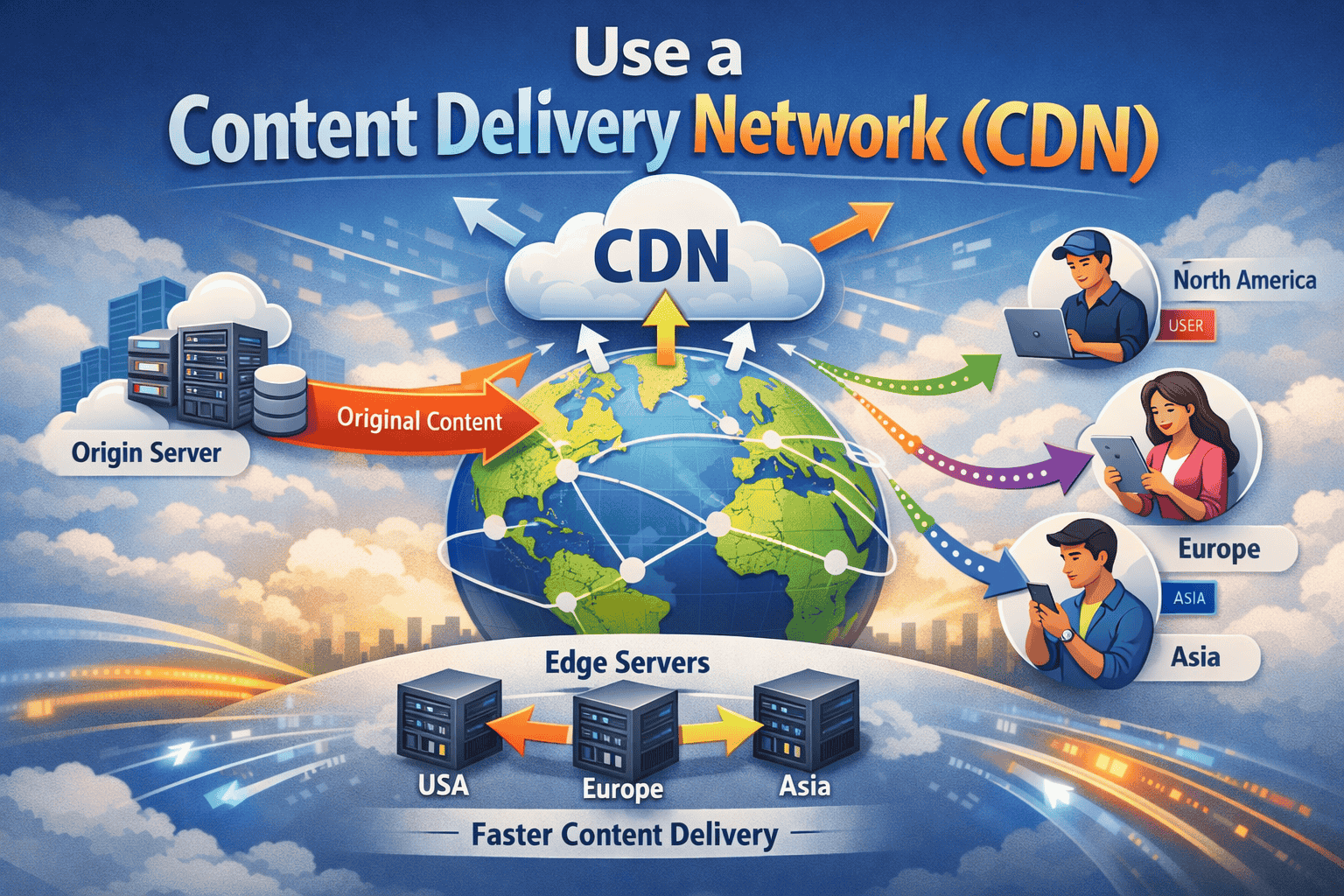
A CDN stores copies of your website on servers around the world. When a user visits your site, the content is delivered from the nearest server, reducing latency and load times. Popular CDNs include Cloudflare, Akamai, and StackPath. CDNs also protect against traffic spikes and DDoS attacks.
5. Reduce Server Response Time
Server response time, or Time To First Byte (TTFB), measures how long it takes for your server to respond to a request. Slow servers can bottleneck your website. Optimize your hosting environment, use faster web servers like NGINX, and consider upgrading to SSD hosting for better performance.
6. Implement Lazy Loading
Lazy loading delays the loading of images and videos until they are visible on the user’s screen. This reduces initial page load time and saves bandwidth. Most modern CMS platforms support lazy loading through plugins or built-in features.
7. Remove Render-Blocking Resources
CSS and JavaScript that block the rendering of your page can slow down perceived load time. Identify render-blocking resources using Google PageSpeed Insights and move critical CSS inline, defer non-essential JavaScript, or use asynchronous loading techniques.
8. Optimize Your Web Hosting
Not all web hosting is created equal. Shared hosting can be slow due to multiple websites sharing server resources. Consider upgrading to VPS or dedicated hosting if your website experiences heavy traffic. Reliable hosting providers ensure faster server response and better uptime.
9. Enable GZIP Compression
GZIP compression reduces the size of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript files before sending them to the browser. Enabling GZIP can reduce file sizes by up to 70%, resulting in faster load times. You can enable GZIP via your server settings or plugins.
10. Reduce Redirects
Excessive redirects create additional HTTP requests, which slow down your website. Audit your website for unnecessary redirects and remove them. Use 301 redirects only when necessary and ensure they chain efficiently.
11. Use HTTP/2
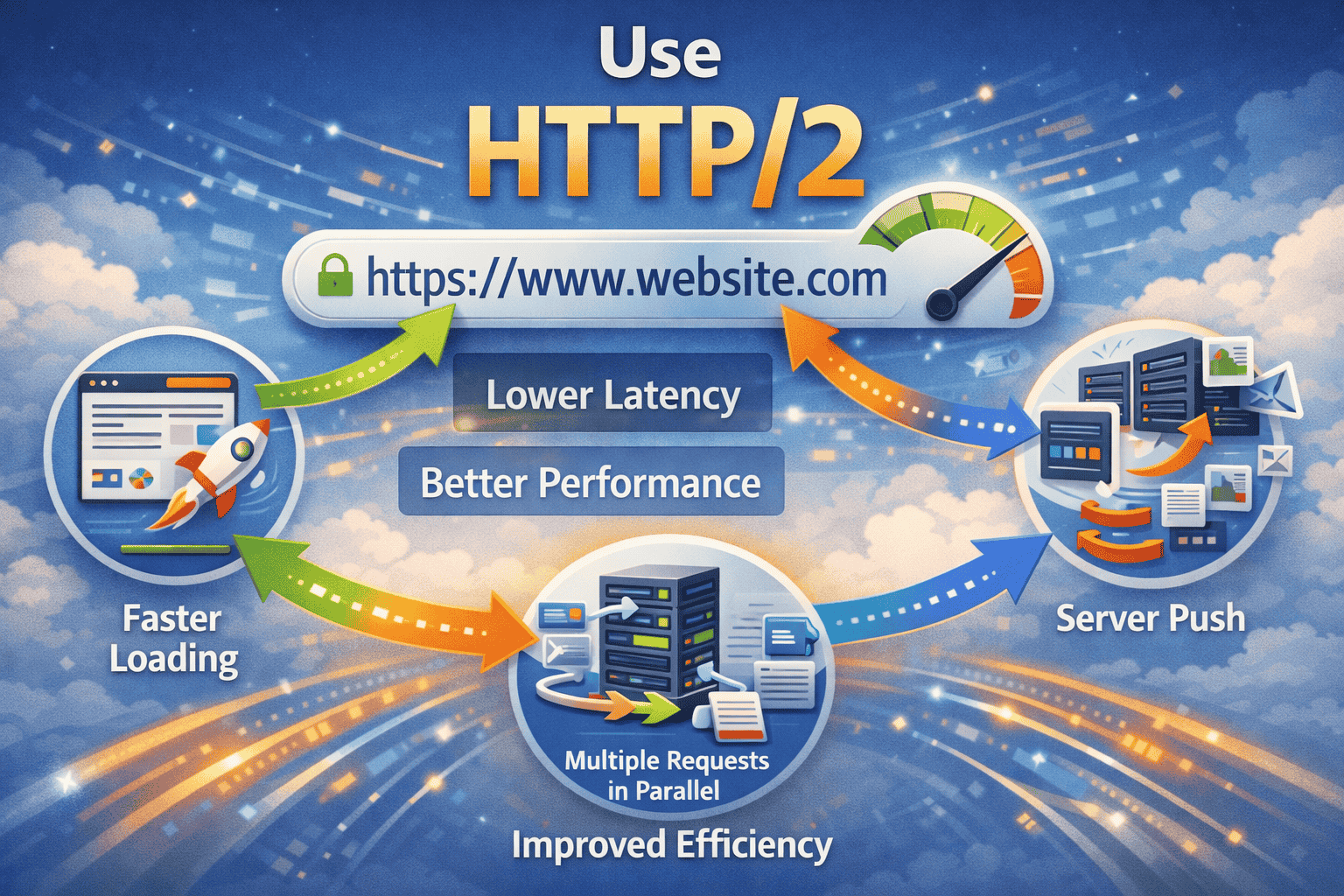
HTTP/2 allows multiple requests to be sent simultaneously over a single connection, reducing latency and improving load times. Ensure your hosting supports HTTP/2 and that your SSL certificate is active, as HTTP/2 requires HTTPS.
12. Optimize CSS Delivery
Instead of loading large CSS files for every page, split your CSS into critical and non-critical parts. Load the critical CSS inline to render above-the-fold content quickly, and defer the rest to load later. This improves perceived page speed.
13. Reduce External Scripts
Third-party scripts like ads, analytics, and social media widgets can slow your site. Audit and limit unnecessary external scripts. Use asynchronous or deferred loading where possible to prevent them from blocking your main content.
14. Enable Keep-Alive
Keep-Alive maintains an open connection between the browser and server, allowing multiple requests without reopening a new connection. Most modern web servers support Keep-Alive by default, but it’s important to ensure it’s enabled for faster performance.
15. Optimize Database Performance
Websites, especially CMS-based ones, rely on databases. Over time, databases accumulate unnecessary data, slowing down queries. Regularly clean and optimize your database using plugins like WP-Optimize or via manual MySQL optimization. Indexing important tables also improves query performance.
16. Implement AMP (Accelerated Mobile Pages)
AMP is a Google-backed framework that creates lightweight, fast-loading versions of web pages for mobile users. Implementing AMP can dramatically improve mobile page speed, which is crucial as mobile traffic dominates the internet.
17. Use a Fast Theme or Framework
Heavy themes with bloated code can slow down websites. Choose lightweight themes or frameworks optimized for speed. For WordPress, themes like GeneratePress, Astra, or OceanWP are known for speed and efficiency.
18. Reduce HTTP Requests
Each file loaded by your website—images, scripts, CSS—creates an HTTP request. Fewer requests mean faster loading. Combine CSS and JavaScript files, use image sprites, and minimize the use of unnecessary plugins or resources.
19. Monitor Website Speed Regularly

Website speed isn’t a one-time task. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Pingdom to monitor performance regularly. Track improvements, identify bottlenecks, and adjust website speed optimization as needed.
20. Implement Caching Plugins (for CMS Websites)
For WordPress and other CMS platforms, caching plugins like W3 Total Cache, WP Rocket, or LiteSpeed Cache can significantly improve speed. They store static versions of pages, reduce server load, and improve response times.
Conclusion
website speed optimization is essential for user experience, SEO, and business growth. By implementing these 20 fixes, you can make your website faster, more efficient, and more enjoyable for visitors. Start with the easiest fixes, like image optimization and caching, then move toward more technical improvements such as database optimization and HTTP/2. Regular monitoring and maintenance ensure your website remains fast as it grows.

