Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Your Sitemap Isn’t Showing in Google Search Console (And How to Fix It)
An XML sitemap helps search engines understand your website structure and discover your pages faster. But sometimes, after submitting your sitemap in Google Search Console, it doesn’t appear, shows an error, or says “Couldn’t fetch.” This can be confusing, especially when you are trying to improve your SEO.

In this blog, we will explain why your sitemap isn’t showing in Google Search Console and how you can fix the problem step by step.
Sitemap URL Is Incorrect One of the most common reasons is submitting the wrong sitemap URL. Even a small mistake like missing “https” or adding an extra slash can cause issues.
How to Fix It:
- Make sure your sitemap URL is correct (example: https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml).
- Open the sitemap in your browser to check if it loads properly.
- Resubmit the correct URL in Google Search Console.
Sitemap Is Blocked by Robots.txt If your robots.txt file blocks search engines from accessing your sitemap, Google won’t be able to fetch it.
How to Fix It:
- Check your robots.txt file (https://yourwebsite.com/robots.txt).
- Make sure there is no “Disallow” rule blocking the sitemap.
- Add this line if missing:
Sitemap: https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
Sitemap Contains Errors Sometimes the sitemap file has formatting errors or broken URLs. If the XML structure is incorrect, Google will not process it.
How to Fix It:
- Validate your sitemap using an online XML validator.
- Remove broken or redirected URLs.
- Make sure the sitemap follows the correct XML format.
Website Is Not Verified in Google Search Console If your website property is not verified, your sitemap submission may not work properly.
How to Fix It:
- Go to Google Search Console.
- Verify ownership using HTML file, DNS record, or Google Analytics method.
- After verification, resubmit your sitemap.
Server or Hosting Issues If your server is slow or temporarily down, Google may not be able to access your sitemap.
How to Fix It:
- Check if your website is loading properly.
- Contact your hosting provider if there are server errors.
- Try submitting the sitemap again after some time.
Sitemap Is Too Large Google has limits for sitemap files. If your sitemap exceeds 50MB or contains more than 50,000 URLs, it may not process correctly.
How to Fix It:
- Split your sitemap into multiple smaller sitemaps.
- Create a sitemap index file.
- Submit the sitemap index in Google Search Console.
Sitemap Missing in Search Console? Here’s What Went Wrong
An XML sitemap plays an important role in helping search engines discover and crawl your website pages. When your sitemap is missing or not appearing in Google Search Console, it can slow down indexing and affect your SEO performance.
If your sitemap is not showing, there is usually a technical reason behind it. Let’s understand what might have gone wrong and how you can fix it.
You Submitted the Wrong Sitemap URL Sometimes the problem is very simple — the sitemap URL entered in Search Console is incorrect. Even a small typo, wrong protocol (HTTP instead of HTTPS), or extra characters can prevent Google from finding it.
What to Do:
- Double-check the exact sitemap URL.
- Open it in your browser to see if it loads properly.
- Make sure you are submitting the correct version (HTTPS or WWW/non-WWW).
Sitemap Is Not Accessible If your sitemap file returns a 404 error, 403 error, or server issue, Google cannot fetch it.
What to Do:
- Check if the sitemap opens without errors.
- Ensure your hosting server is working properly.
- Fix broken links or permission issues.
Blocked by Robots.txt Your robots.txt file might accidentally block search engines from accessing the sitemap.
What to Do:
- Visit yourwebsite.com/robots.txt
- Make sure there is no “Disallow” rule blocking the sitemap.
- Add this line if missing:
Sitemap: https://yurwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
Website Property Not Verified If your site is not properly verified in Google Search Console, your sitemap may not be processed.
What to Do:
- Verify your property using DNS, HTML file, or tag method.
- Make sure you are using the correct property (Domain or URL prefix).
Sitemap Has Formatting Errors An invalid XML structure or incorrect tags can cause Google to reject your sitemap.
What to Do:
- Validate your sitemap using an XML validator.
- Remove broken, redirected, or non-canonical URLs.
- Ensure the sitemap follows proper XML formatting standards.
Common Reasons Your XML Sitemap Is Not Detected by Google
An XML sitemap helps search engines discover and crawl your website pages more efficiently. But sometimes, even after creating and submitting it in Google Search Console, Google does not detect it. This can delay indexing and affect your SEO performance.
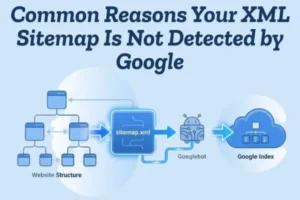
Let’s explore the most common reasons why your XML sitemap is not detected by Google and how you can fix them.
Incorrect Sitemap URL One of the most common mistakes is submitting the wrong sitemap URL. A small error like using HTTP instead of HTTPS or missing “www” can prevent Google from accessing it.
Solution:
- Double-check the sitemap URL.
- Open it in your browser to confirm it loads.
- Submit the correct URL version in Search Console.
Sitemap File Is Not Publicly Accessible If your sitemap requires login access or is blocked by permissions, Google cannot crawl it.
Solution:
- Ensure the sitemap is publicly accessible.
- Remove password protection if applied.
- Check for 403 or 404 errors.
Blocked by Robots.txt Your robots.txt file may accidentally block Googlebot from accessing the sitemap or important pages listed inside it.
Solution:
- Visit yourwebsite.com/robots.txt
- Make sure there is no “Disallow” directive blocking the sitemap.
- Add the sitemap link in robots.txt:
Sitemap: https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
XML Formatting Errors If your sitemap contains invalid XML structure, missing tags, or incorrect encoding, Google may reject it.
Solution:
- Validate the sitemap using an XML validator tool.
- Fix broken URLs.
- Ensure proper XML structure and UTF-8 encoding.
Website Not Verified in Search ConsoleIf your website property is not verified properly in Google Search Console, the sitemap submission may not work.
Solution:
- Verify ownership using DNS, HTML file upload, or tag method.
- Make sure you are using the correct property type (Domain or URL prefix)
Troubleshooting Sitemap Visibility Issues in Google Search Console
An XML sitemap is essential for helping search engines crawl and index your website efficiently. But sometimes, after submitting your sitemap in Google Search Console, it doesn’t appear, shows an error, or says “Couldn’t fetch.”
If you are facing sitemap visibility issues, don’t worry. Most problems are technical and easy to fix. Let’s go step by step.
Check If the Sitemap URL Is Correct
A small mistake in the sitemap URL can prevent Google from detecting it. Using HTTP instead of HTTPS or submitting the wrong version (www vs non-www) can cause issues.
What You Should Do:
Open your sitemap in a browser (example: https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml).
Make sure it loads without errors.
Submit the exact same URL in Search Console.
Verify Website Property
If your website is not properly verified in Google Search Console, your sitemap may not process correctly.
Confirm that you have verified ownership.
Ensure you are using the correct property type (Domain Property or URL Prefix).
Re-submit the sitemap after verification.
Inspect Robots.txt File
Your robots.txt file might block Googlebot from accessing your sitemap or important URLs.
Fix:
- Visit: yourwebsite.com/robots.txt
- Make sure there is no “Disallow” rule blocking your sitemap.
- Add this line if missing:
Sitemap: https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
Check for XML Errors
Google requires a properly formatted XML file. Even a small syntax mistake can stop it from being processed.
Fix:
- Use an XML validation tool to check errors.
- Remove broken or redirected URLs.
- Ensure correct XML structure and UTF-8 encoding.
Look for Server Errors
If your server is slow or temporarily down, Google may fail to fetch your sitemap.
Fix:
- Check if your website loads properly.
- Test your sitemap response code (should be 200 OK).
Technical Errors That Prevent Your Sitemap from Being Recognized
Submitting your sitemap in Google Search Console is an important step for improving your website’s visibility. However, sometimes Google does not recognize your sitemap due to technical issues. These problems are usually simple but require careful checking. Below are the most common technical errors explained with proper headings and paragraphs.

Incorrect Sitemap URL
One of the most common technical mistakes is submitting the wrong sitemap URL. If you enter the wrong version of your website (HTTP instead of HTTPS, or www instead of non-www), Google may fail to access it. Even a small typo in the URL can cause the sitemap to be ignored. Always double-check that the submitted URL matches your actual website version and loads correctly in a browser.
Server Response Errors
If your sitemap returns errors like 404 (Not Found) or 403 (Forbidden), Google will not be able to fetch it. This usually happens when the file is missing, incorrectly uploaded, or blocked by server permissions. Your sitemap must return a 200 OK status to be successfully recognized. Checking your server response can quickly identify this issue
Robots.txt Blocking the Sitemap
Sometimes your robots.txt file accidentally blocks search engines from accessing your sitemap or important directories. If Googlebot is restricted from crawling certain areas, it may not detect your sitemap properly. Reviewing your robots.txt file and ensuring there are no “Disallow” rules blocking the sitemap can solve this issue.
Invalid XML Formatting
Google only accepts properly structured XML files. If your sitemap contains missing tags, incorrect nesting, or invalid characters, it will not be processed. XML formatting errors are common when sitemaps are manually edited. Using an XML validation tool can help identify and fix these structural mistakes.
How to Fix a Sitemap That Doesn’t Appear in Search Console
An XML sitemap helps search engines discover and crawl your website pages more efficiently. But sometimes, after submitting it in Google Search Console, it does not appear or shows errors. This can delay indexing and affect your SEO performance.
If your sitemap is not appearing, don’t worry. Below are the most effective fixes explained step by step.
Check the Sitemap URL
The first thing you should do is verify the sitemap URL. Many times, the issue happens because of a small mistake in the URL — such as using HTTP instead of HTTPS or submitting the wrong version (www vs non-www).
Open your sitemap in a browser (for example: https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml). If it doesn’t load properly, Google will not be able to fetch it either. Make sure the exact working URL is submitted in Google Search Console.
Make Sure the Sitemap Is Accessible
Your sitemap must be publicly accessible. If it is password-protected, blocked by permissions, or returning errors like 404 or 403, Google will not process it.
Check that:
- The sitemap file exists on your server
- It loads without any error
- It returns a 200 OK response
If there are server issues, contact your hosting provider.
Review Your Robots.txt File
Sometimes the robots.txt file blocks search engines from accessing the sitemap or important pages listed inside it. This prevents Google from recognizing the sitemap.
Visit yourwebsite.com/robots.txt and ensure:
- There is no “Disallow” rule blocking the sitemap
- The sitemap URL is clearly mentioned in the file
Adding this line can help:
Sitemap: https://yourwebsite.com/sitemap.xml
Fix XML Formatting Errors
Google only accepts properly structured XML files. If your sitemap contains broken tags, invalid characters, or incorrect formatting, it will not appear in Search Console.
Use an XML validator tool to check:
- Proper opening and closing tags
- Correct encoding (UTF-8)
- No broken URLs
Fix any errors before resubmitting.
Avoid Redirected Sitemap URLs
If your sitemap URL redirects (for example, from HTTP to HTTPS), Google may not process it correctly. Always submit the final destination URL directly.
Using the correct canonical version of your sitemap improves recognition.
From Submission to Visibility: Solving Sitemap Issues in GSC
Submitting your sitemap is only the first step. Many website owners upload their sitemap in Google Search Console and expect instant results. However, sometimes the sitemap does not appear, shows errors, or fails to process.

If your sitemap is stuck between submission and visibility, here’s how to solve the issue step by step.
Confirm Successful Submission
After submitting your sitemap in GSC, always check the “Sitemaps” section to confirm its status. If it shows “Couldn’t fetch” or “Has errors,” it means Google is unable to access or process the file.
Make sure the exact sitemap URL you submitted is correct and matches your website’s live version (HTTPS, www, or non-www).
Review Robots.txt Configuration
Sometimes the problem is not the sitemap itself, but the robots.txt file blocking access. If Googlebot is restricted from crawling the sitemap or important directories, visibility issues can occur.
Check your robots.txt file and ensure:
- No “Disallow” rule blocks the sitemap
- The sitemap URL is mentioned clearly
Adding the sitemap link inside robots.txt can improve discovery.
Validate XML Structure
Google only processes properly formatted XML files. Even small syntax errors can stop your sitemap from appearing.
Common XML issues include:
- Missing closing tags
- Incorrect nesting
- Broken URLs
- Wrong encoding format
Use an XML validator tool to ensure the file is clean and structured correctly.
Check for Redirects
If your sitemap URL redirects from HTTP to HTTPS (or between www and non-www), Google may fail to process it properly.
Always submit the final, direct URL without any redirection. A clean and stable sitemap link improves recognition speed.
Ensure URLs Are Indexable
If your sitemap contains:
- “noindex” pages
- Redirected URLs
- 404 pages
- Non-canonical URLs
Google may treat it as low quality and ignore it. Only include important, indexable, and canonical pages in your sitemap.
Respect Google’s Size Limits
Google allows:
- Maximum 50,000 URLs per sitemap
- Maximum 50MB file size
If your sitemap exceeds these limits, split it into smaller files and create a sitemap index file. Then submit the index file instead.
Sitemap Submitted but Not Showing? Step-by-Step Solutions
Submitting your sitemap in Google Search Console is an important step for improving your website’s indexing. But sometimes, after submission, the sitemap does not appear or shows errors. This can be frustrating, especially when you are trying to improve your SEO performance.
If your sitemap is submitted but not showing, follow these step-by-step solutions to fix the issue.
Check the Submitted URL Carefully
The most common mistake is entering the wrong sitemap URL. Even a small typo, wrong protocol (HTTP instead of HTTPS), or incorrect domain version (www vs non-www) can cause the sitemap to fail.
Open your sitemap in a browser and confirm it loads correctly. Then make sure you submit the exact working URL inside Google Search Console.
Ensure the Sitemap Is Publicly Accessible
If your sitemap is blocked, password-protected, or returning errors like 404 or 403, Google will not be able to process it.
Make sure:
- The sitemap file exists on your server
- It loads without any error
- It returns a 200 OK status
If there are server issues, contact your hosting provider.
Review Robots.txt File
Sometimes the robots.txt file accidentally blocks Googlebot from accessing the sitemap or important folders.
Visit yourwebsite.com/robots.txt and check that:
- There is no “Disallow” rule blocking the sitemap
- The sitemap URL is clearly mentioned
Adding your sitemap URL in the robots.txt file can improve discovery.
Validate XML Formatting
Google only accepts properly structured XML files. If your sitemap has missing tags, invalid characters, or incorrect formatting, it will not show in Search Console.
Use an XML validation tool to check:
- Proper opening and closing tags
- Correct encoding (UTF-8)
- No broken or redirected URLs
Fix any errors before resubmitting.
Avoid Redirected Sitemap URLs
If the submitted sitemap URL redirects (for example, from HTTP to HTTPS), Google may not process it properly.
Always submit the final destination URL directly without any redirection.
Check Sitemap Size Limits
Google allows:
- Up to 50,000 URLs per sitemap
- Up to 50MB file size
Fixing Sitemap Indexing and Reporting Problems in Search Console
An XML sitemap helps Google discover your website pages, but sometimes you may face indexing and reporting problems after submitting it in Google Search Console. You might see errors, “Couldn’t fetch” messages, or fewer indexed pages than expected.

These issues are common and usually technical. Below is a clear explanation of how to fix sitemap indexing and reporting problems step by step.
Understanding the Difference Between Submission and Indexing
Submitting a sitemap does not guarantee that all pages will be indexed. The sitemap only helps Google discover URLs. Google still evaluates each page based on quality, technical setup, and crawl accessibility.
If your sitemap is submitted but pages are not indexed, the problem may not be the sitemap itself but the pages inside it.
Check Sitemap Status in Search Console
Start by going to the Sitemaps section in Search Console. Look at the status message carefully.
Common issues include:
- Couldn’t fetch
- Has errors
- URLs not indexed
Click on the sitemap to review detailed error reports. This will help you understand whether the issue is technical or related to page quality.
Fix Crawl and Server Errors
If Google cannot access your sitemap or pages, indexing will fail. Server errors such as 404, 403, or 500 responses can prevent proper crawling.
Make sure:
- Your sitemap returns a 200 OK status
- Your pages are loading correctly
- Your hosting server is stable and fast
Fixing server issues often resolves reporting problems quickly.
Remove Non-Indexable URLs from Sitemap
Your sitemap should only include indexable pages. If it contains:
- Pages with “noindex” tags
- Redirected URLs
- 404 pages
- Duplicate or non-canonical URLs
Google may ignore them or show indexing errors.
Clean your sitemap and include only high-quality, canonical, and accessible URLs.