Table of Contents
ToggleMastering Robots.txt
Mastering robots.txt is an important step in learning technical SEO. It is a small text file, but it helps search engines understand how to crawl your website properly.

What Is Robots.txt?
Robots.txt is a file placed in the root folder of your website (example: yourwebsite.com/robots.txt). It gives instructions to search engine bots about which pages they can crawl and which pages they should not access.
When a search engine like Google visits your site, it checks the robots.txt file first.
Why It Is Important
Robots.txt helps:
- Control website crawling
- Block unnecessary pages
- Protect admin or private sections
- Improve crawl efficiency
You can also check and test your file using Google Search Console.
Basic Commands
The main commands used in robots.txt are:
User-agent – Defines which bot the rule applies to
Disallow – Blocks a page or folder from crawling
Allow – Allows a page to be crawled
Sitemap – Shows the location of your XML sitemap
How Robots.txt Controls Search Engine Crawling
Robots.txt works like a traffic controller for your website. It guides search engine bots and tells them where they can go and where they should stop. Without it, bots may crawl every accessible page — even the ones that are not important for SEO.
The First File Search Engines Check Whenever a search engine such as Google visits a website, it first checks the robots.txt file. This file is located in the root directory (example: yourwebsite.com/robots.txt).
Before crawling any page, the bot reads the instructions written in this file.
Setting Clear Rules for Bots
Robots.txt controls crawling by using simple commands:
- User-agent – Identifies which bot the rule applies to
- Disallow – Blocks certain pages or folders
- Allow – Grants permission to crawl specific pages
- Sitemap – Directs bots to the website’s sitemap
These rules clearly define which parts of the website are open for crawling and which are restricted.
Focusing on Important Pages
Search engines do not crawl unlimited pages at once. They use a limited crawl budget. Robots.txt helps guide bots toward valuable content and away from low-priority areas like admin panels, duplicate pages, or internal search results.
This makes crawling more efficient and organized.
A Simple but Powerful Control Tool
Although robots.txt is just a small text file, it plays an important role in technical SEO. By setting proper rules, website owners can control how search engines explore their site and ensure better crawling performance.
Robots.txt Best Practices to Protect and Boost Your SEO
Robots.txt is a small file, but it has a very important role in SEO. It tells search engines how to crawl your website and which areas they should avoid. Many beginners ignore this file, but it can directly affect your website’s visibility. If it is set up correctly, it helps search engines focus on your most important pages. If it is set up incorrectly, it can block important content. That is why understanding robots.txt best practices is very important for every website owner.

Keep Your Robots.txt File Simple and Clear
One of the best practices is to keep your robots.txt file simple. You do not need to add too many complicated rules. A clean and easy structure reduces the chances of mistakes. When the file is simple, search engines can understand your instructions clearly. Complicated rules may accidentally block important pages. Always review your file carefully before uploading it. Simple configuration is safer and more effective for SEO
Do Not Block Important Pages
Another important practice is to make sure you are not blocking valuable pages. Sometimes website owners accidentally block blog posts, service pages, or product pages. When search engines like Google cannot crawl these pages, they may not appear properly in search results. This can reduce your website traffic. Always double-check your “Disallow” rules. Make sure only unimportant or private sections are blocked. Protect your SEO by allowing important content to be crawled.
Block Low-Value and Private Sections
Robots.txt is very helpful for blocking unnecessary areas of your website. You can block admin panels, login pages, test pages, or duplicate content folders. These pages do not need to appear in search results. Blocking them saves crawl budget and improves crawling efficiency. It also keeps search engines focused on your main content. However, remember that robots.txt is not a security tool. It only guides bots, not real users.
Always Add Your Sitemap
Adding your XML sitemap link inside robots.txt is a smart SEO practice. It helps search engines quickly find your important pages. This improves crawling speed and page discovery. You can also check and test your robots.txt file using Google Search Console. Regular testing ensures there are no errors. A properly added sitemap supports better indexing and overall SEO performance.
Understand That Robots.txt Controls Crawling, Not Indexing
Many beginners think robots.txt removes pages from search results, but this is not completely true. Robots.txt only controls crawling. If you want to prevent a page from appearing in search results, you should use a noindex meta tag. Understanding this difference is very important. Using the correct method will protect your website from SEO problems. When used wisely, robots.txt becomes a powerful tool for managing your site’s visibility.
Common Robots.txt Mistakes That Hurt Website Rankings
Robots.txt is a small file, but even a small mistake in it can seriously affect your website rankings. Many website owners create this file once and never check it again. Because of this, important pages may get blocked without notice. When search engines cannot properly crawl your content, your visibility in search results can decrease. Understanding common robots.txt mistakes can help you protect your SEO performance.
Blocking the Entire Website
One of the biggest mistakes is accidentally blocking the entire website. This usually happens when someone uses the command “Disallow: /”. It tells search engines not to crawl any page on the site. Sometimes developers use this during website development and forget to remove it. When search engines like Google see this rule, they stop crawling completely. As a result, rankings and traffic can drop quickly.
Blocking Important Pages or Folders
Another common mistake is blocking valuable pages such as blog posts, product pages, or service pages. If these pages are disallowed, search engines cannot properly crawl them. This means your important content may not perform well in search results. Always double-check your “Disallow” rules before publishing changes. Even a small folder-level block can affect many URLs. Careful review helps prevent ranking loss.
Blocking CSS and JavaScript Files
Some website owners block CSS or JavaScript folders without realizing the impact. Search engines need access to these files to understand and render your website properly. If they cannot load these resources, your site may not appear correctly in search results. This can negatively affect user experience and rankings. Always make sure essential resources are allowed for crawling.
Confusing Robots.txt with Noindex
Many beginners think robots.txt removes pages from search results. This is not completely correct. Robots.txt controls crawling, not indexing. If you want to stop a page from appearing in search results, you should use a noindex meta tag. Understanding this difference prevents SEO mistakes. Using the wrong method can cause unexpected ranking issues.
Advanced Robots.txt Rules for Technical SEO Optimization
Robots.txt is not only for basic blocking of admin pages. When used strategically, it becomes a powerful technical SEO tool. Advanced rules help you control crawl behavior, manage crawl budget, and guide search engines toward high-value content. For larger websites especially, smart configuration can improve overall site performance and indexing efficiency.
Using Wildcards for Better Control
Advanced robots.txt rules allow you to use wildcards like * to control multiple URLs at once. This is helpful for blocking dynamic parameters, filter URLs, or duplicate pages. Instead of blocking each URL manually, you can create one rule that covers many variations. This keeps your file clean and efficient. It is especially useful for eCommerce or large content websites.
Managing URL Parameters and Duplicate Content
Many websites generate URLs with parameters such as sorting, filtering, or tracking codes. These URLs often create duplicate content. By carefully blocking unnecessary parameter-based URLs, you help search engines focus only on the main version of your content. Search engines like Google then spend crawl budget more efficiently. This supports stronger technical SEO optimization.
Controlling Specific Bots
Robots.txt allows you to create rules for specific user agents. For example, you can allow general search engine bots but restrict certain bots if needed. This level of control is useful for managing server load or limiting unwanted crawlers. It gives website owners more flexibility in handling traffic from different bots.
Optimizing Crawl Budget for Large Websites
Large websites often face crawl budget limitations. Advanced robots.txt rules help block low-value sections such as internal search results, tag pages, or duplicate archives. By doing this, you guide search engines to prioritize important landing pages, categories, and core content. This improves crawl efficiency and indexing speed.
Combining Robots.txt with Other SEO Tools
Advanced optimization does not rely on robots.txt alone. It works best when combined with proper sitemap management and regular testing. Tools like Google Search Console help monitor crawl activity and identify blocked URLs. Reviewing reports ensures that your advanced rules are working correctly and not harming important content.
How to Create an SEO-Friendly Robots.txt File
Creating an SEO-friendly robots.txt file is important for guiding search engines to crawl the right parts of your website. A well-structured file improves crawl efficiency and prevents important pages from being blocked accidentally. Below are simple steps and best practices to help you create one correctly.
Place the File in the Root Directory
- Create a plain text file and name it robots.txt
- Upload it to your website’s root folder (example: yourwebsite.com/robots.txt)
- Make sure it is publicly accessible
- Only one robots.txt file should exist per domain
Search engines like Google will always check this location first.
Start with the User-Agent Rule
- Use User-agent: * to apply rules to all bots
- You can also write rules for specific bots if needed
- Keep the format clean and correct
- Avoid spelling or formatting mistakes
This tells search engines which crawler the rules apply to.
Use Disallow Carefully
- Block only low-value or private folders (e.g., /admin/, /login/)
- Do not block important pages like blogs or products
- Double-check folder paths before saving
- Avoid using “Disallow: /” unless intentionally blocking the full site
Incorrect use of Disallow can hurt rankings.
Allow Important Resources
- Make sure CSS and JavaScript files are not blocked
- Allow essential content folders
- Ensure search engines can fully render your website
- Review your rules regularly after updates
Proper access helps search engines understand your site layout.
Add Your Sitemap
- Include your XML sitemap URL
- Place it at the bottom of the file
- Use the full URL format (https://example.com/sitemap.xml)
- Keep the sitemap updated
You can test and monitor your file using Google Search Console to ensure everything works correctly.
Test Before and After Publishing
- Use robots.txt testing tools
- Check that important pages are crawlable
- Fix any warnings or errors immediately
- Monitor crawl reports regularly
Testing prevents accidental SEO issues.
Robots.txt vs Noindex: Understanding the Key Differences
The main difference between robots.txt and noindex is how they control search engines.
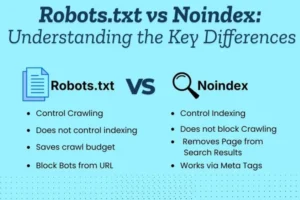
Robots.txt controls crawling.
It tells search engines which pages or folders they are allowed to visit. When a search engine like Google finds a page blocked in robots.txt, it may not crawl that page. However, the page can still appear in search results in some cases if other websites link to it.
Noindex controls indexing.
The noindex tag is placed inside a webpage’s HTML code. It allows search engines to crawl the page but clearly tells them not to include it in search results. Once search engines see the noindex tag, they remove or prevent that page from appearing in rankings.
In simple terms:
- Robots.txt = controls whether a page can be crawled.
- Noindex = controls whether a page can appear in search results.
Robots.txt works at the site or folder level, while noindex works at the individual page level. Understanding this difference helps you use the correct method for your SEO goals.
Blocking the Right Pages: Smart Robots.txt Strategies
Blocking the right pages in robots.txt is an important part of technical SEO. If you block the wrong pages, your rankings can drop. If you block the right ones, you improve crawl efficiency and protect your website. Smart robots.txt strategies help search engines focus only on valuable content.
Focus on Low-Value Pages Not every page on your website needs to be crawled. Pages like admin panels, login areas, internal search results, and test pages do not provide SEO value. Blocking these sections helps search engines avoid wasting crawl budget. This ensures important pages get more attention.
Protect Private and Sensitive Areas
Robots.txt is useful for guiding search engines away from private folders such as:
- /admin/
- /login/
- /checkout/
- Development or staging folders
When search engines like Google crawl your website, they will skip these blocked areas and focus on public content.
Avoid Blocking Important Content A smart strategy also means knowing what not to block. Never block important blog posts, product pages, service pages, or category pages. These are the pages that bring traffic and rankings. Always double-check your Disallow rules before publishing changes.
Manage Duplicate and Filter URLs Large websites often create duplicate URLs through filters or parameters. Instead of letting search engines crawl all variations, you can block unnecessary filtered URLs. This improves crawl efficiency and reduces duplicate content issues.
Regularly Test Your Robots.txt File Even a small mistake in robots.txt can cause big SEO problems. Always test your file after making updates. Tools like Google Search Console help you check if important pages are blocked accidentally. Regular monitoring keeps your SEO safe.
Testing and Fixing Robots.txt Errors in Google Search Console
Testing and fixing robots.txt errors is an important step in maintaining strong SEO performance. The robots.txt file controls how search engines crawl your website, so even a small mistake can block important pages. If key pages are restricted, your rankings and traffic may decrease without you realizing it. That’s why regular testing is necessary.

Using Google Search Console, you can check whether your robots.txt file is causing any crawl issues. Inside the tool, you can review your robots.txt status and inspect specific URLs to see if they are blocked. This helps you quickly identify problems such as incorrect “Disallow” rules or blocked important sections like blogs or product pages.
If you find an error, you need to edit the robots.txt file carefully. Remove or correct the incorrect rules, upload the updated file to your website’s root directory, and then recheck it in Search Console. After fixing the issue, search engines like Google will recrawl your site and update their records.
Regularly monitoring and fixing robots.txt errors ensures that search engines can properly access your valuable content, which supports better crawling, indexing, and overall SEO performance.
How Robots.txt Affects Crawl Budget and Indexing
Robots.txt may look like a small technical file, but it strongly influences how search engines explore your website. It does not directly decide which pages rank, yet it controls how bots move through your site. This movement directly affects crawl budget and indirectly impacts indexing. When used wisely, it improves efficiency. When misused, it can slow down your SEO growth.
Crawl Budget: Why It MattersSearch engines such as Google do not crawl every page of every website endlessly. They assign a limited crawl budget, which means they will only crawl a certain number of pages during each visit.
If your website has many unnecessary or duplicate URLs, bots may spend their crawl budget on those instead of your important pages. As a result, valuable content may not be crawled quickly, delaying visibility in search results.
How Robots.txt Guides Crawling Robots.txt works like a direction map for search engine bots. By blocking low-value areas like admin panels, filter URLs, tag pages, or duplicate folders, you help bots focus on pages that actually matter for SEO.
This smart blocking improves crawl efficiency. Instead of wasting resources, search engines spend more time on your main content such as blog posts, service pages, or product listings.
The Indirect Impact on Indexing Indexing happens after crawling. If a page is not crawled properly, search engines cannot fully understand its content. That means it may not get indexed quickly or ranked properly.
However, robots.txt does not directly remove a page from search results. It only limits crawling access. That is why it must be used carefully to avoid blocking important pages by mistake.
Finding and Fixing Issues If crawl problems occur, tools like Google Search Console help you identify blocked URLs. Regular monitoring ensures your robots.txt file supports your SEO strategy instead of harming it.